In Case You Missed It: Decoding Cybersecurity for MSMEs
Dec 2, 2021
A notification pops up on a business’s computer and says they have several days to pay an amount before all their data is deleted. This business just became a victim of ransomware—a debilitating cyberattack that can shut down entire companies and result in enormous financial losses. How do we protect businesses from experiencing these forms of attacks? DAI’s South Asia Regional Digital Initiative (SARDI), in partnership with the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)’s Indo-Pacific Office, recently hosted a thought-provoking webinar on strengthening the cybersecurity awareness, preparedness, and defense capabilities of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in South Asia. These businesses not only provide substantial employment opportunities in their communities but also contribute enormously to the region’s GDP levels. We felt it was necessary to bring together renowned experts from some of India’s most well-known technology firms as well as India’s Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises to address the region’s pressing cybersecurity risks, solutions, and resources. This webinar was part of the SARDI Dialogue Series of webinars highlighting the opportunities and challenges for South Asia’s MSMEs. SARDI is an activity under DAI’s Digital Frontiers project and part of the Digital Connectivity and Cybersecurity Partnership (DCCP).

Women entrepreneurs in West Champaran, Bihar, India. Credit: Digital Empowerment Foundation.
By Going Digital, MSMEs Increase Their Risk
With as many as 63 million MSMEs in India, it is crucial that these businesses recognize their cyber vulnerabilities and the consequences of a digital attack. Cyberattacks not only have reputational implications but can also result in tremendous financial losses for companies of all sizes. “MSMEs run the risk of losing the trust of their clients. For example, if a business is an e-commerce platform and its customer data is stolen, the MSME will be sure of losing almost all their business,” says Abhishek Singh, CEO of India’s MyGov, President and CEO of the National eGovernance Division and Managing Director and CEO of the Digital India Corporation. Singh added that as employees moved to remote working environments, the risk of data loss and cyberattacks increased.
It is essential that when MSMEs adopt digital tools, both the business’s leadership and employees understand and mitigate the potential new risks including malware, data breaches, phishing, and ransomware. However, successful cybersecurity requires a whole-of-industry approach. Both policymakers and private sector experts must ensure that they are proactively reaching out to a growing community of digitally connected MSMEs—particularly those led by more vulnerable populations. This outreach will ensure that businesses learn about cybersecurity risks early on in their growth stage and understand the available tools. It is through this approach that businesses can safely grow while protecting both their financial assets and reputation.
Building Awareness to Combat Cyber Risk
“MSMEs have always had risk factors as they have been concentrated on business priorities. These businesses want to grow, they don’t have proper resources, and, in many cases, they have very little understanding of cyber threats. This exponentially increases their cyber risk—it is like a low hanging fruit for attackers.”—Gautam Kapoor, Partner Cybersecurity and Risk Advisory, Deloitte.
Due to a lack of awareness, limited resources, and a perceived lack of return on investment, many MSMEs do not devote the dedicated time necessary to comply with rapidly changing cybersecurity standards. However, contrary to common assumptions, cybersecurity protection does not always require rebuilding IT infrastructure or implementing costly solutions. Our speakers pointed out that behavioral changes and awareness are critical first steps to improving cybersecurity protections. Kapoor offered the following tips to MSMEs looking to implement awareness measures in their business practices.
Seven Habits of Cyber-Aware MSMEs
-
Know the exact asset you are trying to protect—is it data, intellectual property, a particular product? Businesses should know exactly what is vulnerable and what needs to be secured.
-
Be aware of certain cybercrimes and cyber risks. For example, how does a phishing attack happen, how do organizations experience ransomware attacks? All employees in the organization should be aware of cyber risks (i.e., do not click on unknown links).
-
Adopt the concept of “never trust, always verify.” Always verify external emails, messages, and electronic sources.
-
Use multi-factor authentication for all applications and devices (including both personal and professional).
-
Use strong passwords—do not use date of birth, name, know numbers, or any personally identifying information.
-
Back up your data—this is the easiest way to protect your company against a ransomware attack.
-
Vulnerability analysis and patching your system—make sure systems are upgraded on a regular basis.
These tips are essential to implementing basic and cost-effective cybersecurity practices. In addition, MSMEs should not disregard their vulnerabilities due to their size. Many small businesses believe that they will not be targeted as they are “not important enough.” These businesses are often surprised when an attack hits them. This misconception held by MSMEs—coined as “security by obscurity” by Samir Datt, Director of the Foundation Futuristic Technologies, during our webinar—reaffirms why MSMEs must pay careful attention to their cybersecurity protections regardless of size. Just because a business is unknown to many, does not prevent it from being the recipient of a cyberattack from a malicious actor. An easy way for MSMEs to build their cybersecurity protections is by following the tips our speakers provided above.
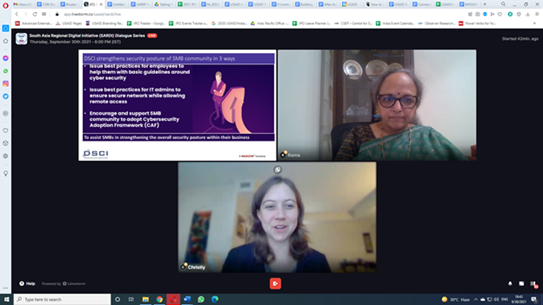
Ms. Rama Vedashree, CEO of Data Security Council of India sharing the DSCI Cyber Adoption Framework for SMBs
SARDI Dialogue Series Panel discussion on the impacts, risks and issues of cyber laws & policies on small businesses in South Asia
Cybersecurity Resources for MSMEs
With an evolving cybersecurity risk landscape for MSMEs, there are many resources offered by the India Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology as well as private cybersecurity companies that allow MSMEs to enhance their awareness of cyber issues, audit their security features, and upgrade their IT infrastructure. Presented by Rama Verdashree, CEO of the nonprofit industry body, the Data Security Council of India (DSCI), during the webinar, the DSCI Cyber Adoption Framework for Small and Medium Businesses is an important and free resource available to MSMEs. DSCI is committed to making cyberspace safe, secure, and trusted by establishing best practices, standards, and initiatives in cybersecurity and privacy. Understanding that businesses are often limited by financial constraints, DSCI provides access for MSMEs to determine their degree of exposure to cyber risks and assess their existing IT infrastructure. By helping businesses analyze the security of their information and other assets, and providing guidelines to safeguard them against cybersecurity risks, DSCI aims to help MSMEs adopt various control measures needed to safely position their companies in an online environment.
Just as DSCI’s framework helps businesses analyze their own level of security and exposure to cyber risk, USAID’s Cybersecurity Primer is a resource for partners, donors, governments, and development practitioners working with MSMEs. The primer introduces the concept of cybersecurity as a development challenge, presents opportunities to integrate cybersecurity throughout programming, and highlights cyber threat trends by sector. Resources such as the Primer and DSCI’s framework are vital in mitigating critical threats that not only harm businesses but also pose destabilization risks to the social and economic ecosystems of partner countries as a whole.
How is Digital Frontiers Supporting MSMEs In South Asia?
Cybersecurity threats exploit the increased complexity and connectivity of regional critical infrastructure systems, placing a nation’s security, economy, and public safety at risk. As part of the DCCP, which aims to increase adoption of cybersecurity best practices in targeted countries, SARDI is working diligently to improve the digital capabilities of MSMEs by increasing cybersecurity awareness and digital upskilling opportunities for businesses in South Asia. MSMEs are an essential focus of SARDI’s work as the program aims to enable businesses to safely participate in the digital economy. Recognizing that COVID-19 further necessitated the use of digital tools and technologies for business operations, SARDI empowers entrepreneurs by engaging them in digital upskilling programming and facilitating cybersecurity discussions to help them better understand, comply with, take advantage of, and think critically about the digital risks and solutions which affect their organizations. Learn more about how this program provides access to resources and information necessary to protect and expand digital businesses in an increasingly digitalized world.
To watch the full webinar, click here.